Collisions with container
One can calculate the number of atomic or molecular collisions with a wall of a container per unit area per unit time.
Assuming an ideal gas, a derivation
[2] results in an equation for total number of collisions per unit time per area:
-
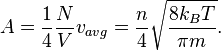
Speed of molecules
From the kinetic energy formula it can be shown that
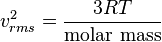
with
v in m/s,
T in kelvins, and
R is the gas constant. The molar mass is given as kg/mol. The most probable speed is 81.6% of the rms speed, and the mean speeds 92.1% (distribution of speeds).
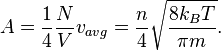
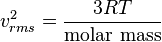
No comments:
Post a Comment